FluBot Android Malware Technical Analysis – Indepth Free guide
FluBot Android Malware Technical Analysis
This great article was published originally at ThreatMonIT web site, and I wanted to ensure you get access to it, and as a result shared it here with the permission of the company
What is BOTNET?
Cyber attackers establish a network by infecting computers with malware. This remotely controlled malware is called a “bot “. The network of these bots is called a “botnet “. These computers are also called zombies.
Sometimes cyber attackers set up a large botnet to make it easier and more organized for attacks to be carried out. The attackers often use an infected email attachment, links, website or physical tools to save malware on the computer. Bots are often used by attackers to DDoS attacks, data theft, distribution of malware, spam mails, and to earn money from advertisements.
What Attackers Do with a Botnet?
Attackers can steal a lot of data from computers included in the botnet network. Attackers sell the data they stole from your computer. These data are specifically usernames and passwords.
Threat actors sell or rent these botnets on the Dark Web & Deep Web or Black Markets. Some attacks can be made with botnets created or purchased by attackers. Botnets are often used for this purpose.

What is a Botnet Attack
Attackers controlling the botnet command the bots to access a website or IP address simultaneously. Website traffic intensifies due to requests from many computers to the specified address. So, the site may crash. This is the DDos attack.
- Botnets can send large volumes of spam emails at once, meaning that botnets can infect large numbers of computers with malware.
- Botnets are used to make brute force attacks faster and get better results.
- Keylogging, another attack technique with botnets, collecting sensitive information about targets.
- Phishing attacks: This is done through large spam campaigns aimed at stealing user account information such as banking logins or email information.
Most attacks on a single computer are also done with botnets. The goal here is to use multiple computers in an attack.
FluBot Android Malware Technical Analysis
The FluBot it’s an Android malware that targets Android devices and spreads to victims via phishing SMS messages that contain the malicious link to download the FluBot app. Victims click on this link and then download a file with an .apk extension. Right after the installation process is completed, the FluBot malware communicates with the command control (C2) server and runs arbitrary codes into Android device remotely.
As a result of the analyzes performed, it was determined that the FluBot malware was able to send SMS, read incoming text messages, kill background applications, and access the phone contact lists on the victim device remotely.
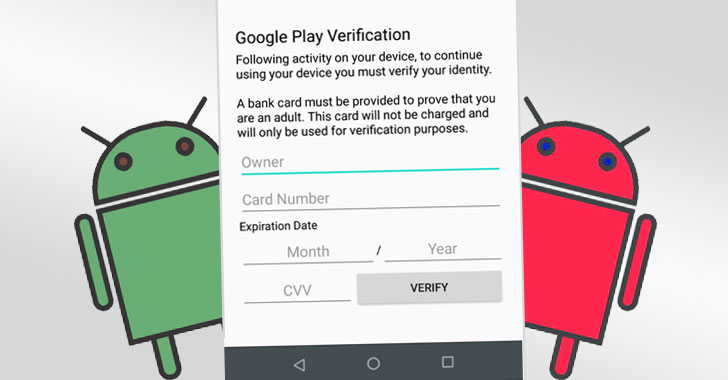
After the installation of FluBot, the malware itself (fake DHL application that’s contain malware) requests some special permissions from victim device. If victim gives these permissions and rights, the malware executes Phishing form in order to collect Banking Information from victim, these data contain (Name-Surname, CVV, Card Number, etc.). If the victim is tricked by attackers and enters these data, it will be uploaded in an unencrypted way into attackers Command And Control server.
Fake DHL SMS notification message (Phishing)
In another example, FluBot malware was installed via Phishing SMS message that contains malicious links. Victim opens this link and gets tricked by attackers to download fake FedEx app (The screenshot of the phishing sample page is as follows.)

Spreading Frequency & Victim Countries
FluBot malware attacks are mostly spread in European Countries. After the COVID pandemic, attackers has abused package delivery services as a phishing tool, so FluBot has a very rapid spreading in such a short time.

FluBot Technical Analysis
After the FluBot malware is downloaded, it asks for user approval to give “full access” authorization in the device for FluBot. Malware continues to run in the background even if the target user closes the application after the approval is given by the target user.

The permission list of the “com.eg.android.AlipayGphone” (FluBot) malware running in the background is as follows:
- android.permission.INTERNET
- android.permission.READ_CONTACTS
- android.permission.WRITE_SMS
- android.permission.READ_SMS
- android.permission.SEND_SMS
- android.permission.RECEIVE_SMS
- android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE
- android.permission.QUERY_ALL_PACKAGES
- android.permission.WAKE_LOCK
- android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE
- android.permission.REQUEST_IGNORE_BATTERY_OPTIMIZATIONS
- android.permission.CALL_PHONE
- android.permission.REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES
- android.permission.KILL_BACKGROUND_PROCESSES
- android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE
The malware that accesses it with the above permissions becomes able to perform the following actions:
- Internet access.
- SMS Reading / Sending.
- Reading the phone book.
- Making a Call.
- Deleting apps from within the device.
- Ability to use the accessibility service.
- Reading device notifications.
The target user’s Android device is now in constant communication with the attacker’s command control server. As a result of our analysis, it has been determined that this communication could be continue over the SOCKS Proxy according to the attacker’s request.

String Obfuscation
The FluBot malware uses the open-source String obfuscator software called Paranoid to make it difficult to examine and easier to bypass anti-virus software, so the malware is given the ability to hide the string data during it’s working phase.
Obfuscated String data:
- BotId
- BrowserActivity
- CardActivity
- ComposeSmsActivity
- ContactItem
- DGA
- ForegroundService
- HttpCom
- IntentStarter
- LangTxt
- MainActivity
- MyAccessibilityService
- MyNotificationListener
- PanelReq
- SmsReceiver
- Spammer
- Utils
- SocksClient
- PanelReq

String De-obfuscate
String data of the FluBot malware are hidden by the attackers, Obfuscated String data must be De-obfuscated for the correct analysis results. An open source Java software was used for this process.

When the Java software was run in order to crack the data, the data in the chunks37 array is understood with a mathematical function and is converted into normal string data. As can be seen on the right, there are String data used in the phishing phase of different languages in the output data. (Card Number, CVV, Owner, Year etc.)

Command And Control (C2 Server)
The newest version of the FluBot malware has emerged as 4.0. After FluBot infects the target Android device, it creates a domain consisting of random numbers and letters with the help of an algorithm called Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) to connect with the attacker, and thus the command control servers of the attackers can be hidden from bot softwares. The connection is done in the form of DNS or DNS over HTTPS, especially in the 4.0 version. Thus, when the malware sends connection request packets to the target device, it avoids the firewall, EDR or Anti-Virus systems.
The rise that started on 2021-01-22 was realized with the 4.0 version.

The Google DNS feature has been abused by the attackers, so Google DNS is used as a tunnel and connection requests are made to the attacker’s Command and Control servers via DNS. The screenshot of HTTP requests is below.

Command And Control servers created with DGA:

The function that performs the connection request made via “poll.php” belonging to FluBot 4.0 version, can remotely run commands (PING, LOG, SMS_RATE, GET_SMS etc.) over the attacker C2 server.

As a result of our analysis, the decompiled function tasked with providing the DNS over HTTPS connection for the FluBot malware to access the target device remotely is given in the picture below.
This method of attack has been chosen especially for targets in Britain and United States. The most important difference is that in a different example of the FluBot 4.0 malware, the attackers can have chosen Cloudflare DNS instead of Google DNS to get connections.

Another feature of the FluBot Malware is being able to perform country-specific attacks using country-based codes found on mobile phone numbers. During the phishing attack, the cargo services and the language spoken in that country are taken into consideration by the attackers and an appropriate interface is chosen that way.

It steals information such as credit card number, CVV, device information from the target user.

After the target user deceive (with the phishing method) enters this information into the form interface in the FluBot malware, String data is transmitted to the attackers with the help of “GetCredential_A05” function.

The form (Phishing form) for the data requested by the FluBot malware from the target user is in the image below.

FluBot 3.7 Version of HTTP Traffic Analysis
To capture the HTTP connection with Burp Suite Proxy, JavaScript code is injected into the malicious software by using Frida, thus the connection can be captured, and Android SSL Pinning is bypassed. When the connection wass examined, it is observed that connection requests is sent from the target device with string data encoded with base64 over poll.php. Attackers can communicate with the victim device instantly with POST and GET requests.

IOC Data
FluBot v3.7
| Phishing Correos Hash Data |
| 446833e3f8b04d4c3c2d2288e456328266524e396adbfeba3769d00727481e80 |
| bb85cd885fad625bcd2899577582bad17e0d1f010f687fc09cdeb8fe9cc6d3e1 |
| 8c14d5bc5175c42c8dd65601b4964953f8179cfe5e627e5c952b6afd5ce7d39d |
| Phishing Fedex Hash Data |
| a601164199bbf14c5adf4d6a6d6c6de20f2ab35ec7301588bceb4ee7bb7d1fdc |
| f0fa95c3b022fb4fee1c2328ffbc2a9567269e5826b221d813349ebf980b34da |
| 07ba6893c4ffc95638d4d1152f7c5b03aca4970474a95bf50942c619aa4382ae |
| ca5ba6098a2a5b49c82b7351920966009a99444da4d6f6e5a6649e5e2aeb3ff8 |
| 8be8576c742f31d690d449ab317b8fb562d03bc7c9dc33fa5abf09099b32d7a0 |
| Phishing DHL Hash Data |
| 54ecabbff30b05a6a97531f7dec837891ce49ae89878eaf38714c1874f5f1d15 |
| c3838f9544e613917068f1b2e22ab647fd5a60701e1045b713767a92cf79f983 |
| ab29813b1da1da48b4452c849eedc35b6c52044946d39392530573c540916f74 |
FluBot v4.0
| Phishing DHL Hash Data |
| 3a4bdcb1071e8c29c62778101b7ae8746f3ee57cb1588e84d7ee1991964703e6 |
| 22025590bbb4d3a30658fea45a936b6a346479c83d1c35f85521a1ac564342a0 |
| 774acbfbedd2a37e636f6251af84a7abb2e64c2db9d6de5ce0fec4121064ea49 |
| 3bf82acb8d511bfef3e083b73136824aab3612b516f150d916fe351b7e5bc9d3 |
| 9b9b67a2b9ec5a15044430a9f5d9ce6a7f524e1feed186a96309256df686cfdd |
| 8bb8b1a1dc1487db610700f6b59ea4ab44ddc2f52e0eca06f8d1da663b312b58 |
To read more Cybersecurity related articles click here





